Understanding horse genders is essential for horse riders, breeders, and enthusiasts alike. It’s not just about identifying if a horse is male or female; it encompasses understanding the unique needs, behaviors, and characteristics that vary across different ages and types of horses.
Whether you’re a seasoned equestrian or a new horse owner, grasping the intricacies of horse genders can significantly enhance your relationship with these majestic animals.
Horse genders play a crucial role in horse care, training, and overall well-being. However, many horse owners and riders often face confusion when it comes to distinguishing and understanding different horse genders.
Have you ever wondered why your colt behaves differently from your mare? Or why your gelding seems calmer compared to a stallion?
This guide aims to demystify horse genders by comparing them across various ages, providing a comprehensive understanding that will help you manage and care for your horses more effectively.
Horse Genders Explained
Horse genders are categorized based on their reproductive organs and sometimes their behavioral characteristics. Here’s a breakdown of the primary horse genders:
Stallion
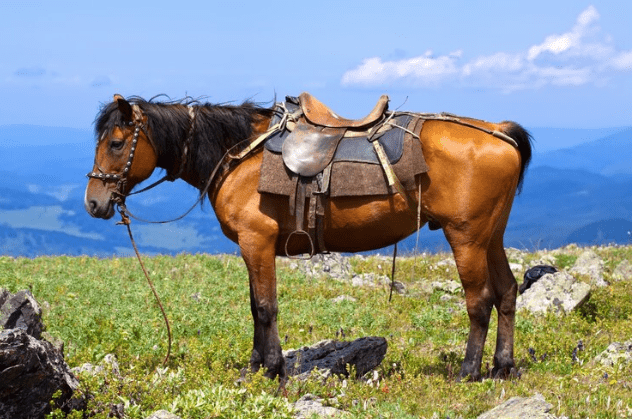

A stallion is a mature, uncastrated male horse, typically over four years old. Stallions are known for their strong, muscular build and often exhibit more aggressive and dominant behavior compared to other horse genders. They are primarily used for breeding purposes due to their intact reproductive organs.
Mare
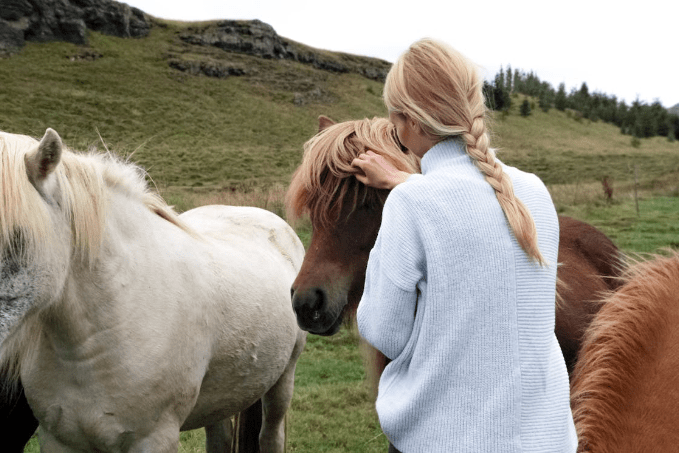

A mare is an adult female horse, usually over the age of three. Mares can be used for breeding, riding, and various work purposes. They tend to be more nurturing, especially towards their foals, but can also exhibit strong-willed behavior. People love Boltaki as white horse names in the mare category.
Gelding
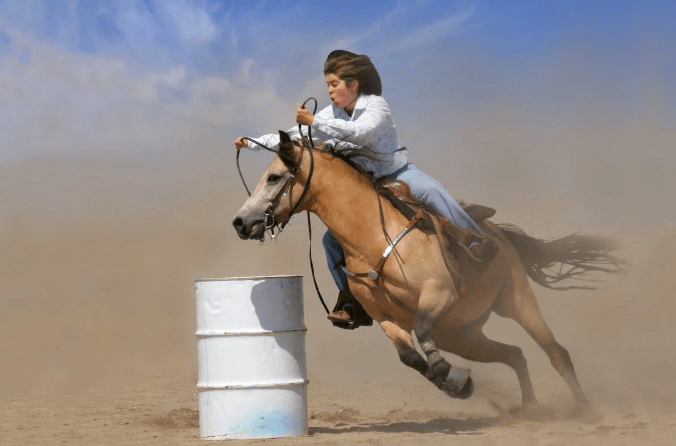

A gelding is a castrated male horse of any age. Geldings are known for their calm and steady temperament, making them ideal for riding and work purposes. The castration process reduces aggressive and dominant behaviors often seen in stallions.
Colt
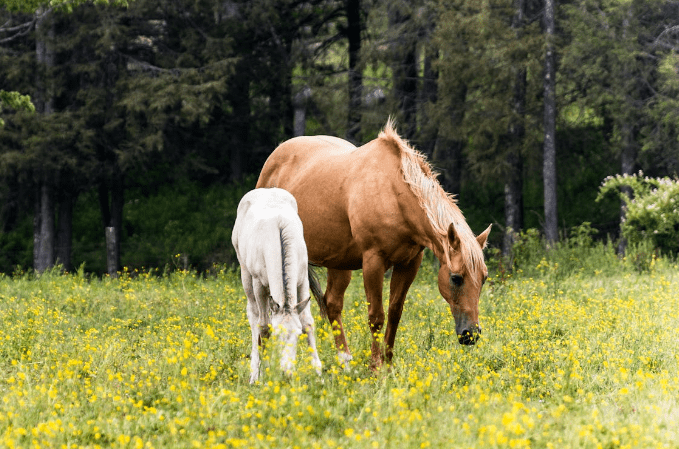

A colt is a young male horse, typically under the age of four. Colts are energetic and can be more challenging to handle due to their youthful exuberance and developing hormones. Proper training and socialization are crucial during this stage.
Filly

A filly is a young female horse, usually under the age of four. Fillies can be playful and curious, and like colts, they require proper training to ensure they grow into well-behaved adults.
Foal
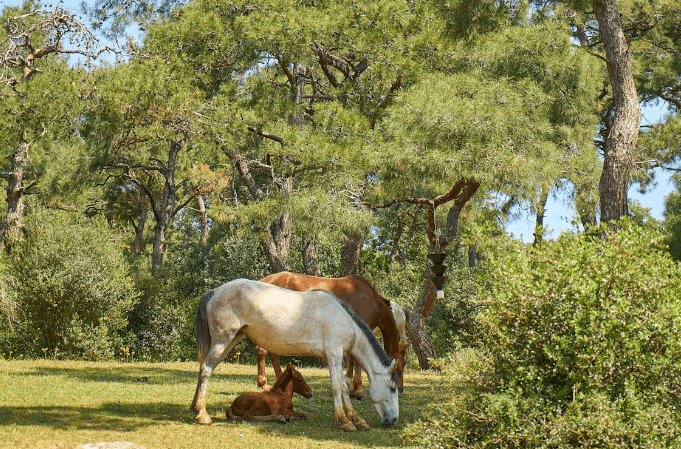
A foal is a young horse of either gender, usually under the age of one. Foals are dependent on their mothers and require careful handling and nurturing to ensure healthy development.
Different Horse Genders
Understanding the different horse genders is essential for proper horse names, horse care and training. Each gender has unique characteristics and requirements that need to be considered.
Stallion vs. Gelding
Stallions and geldings exhibit significant differences due to the presence or absence of reproductive organs. Stallions, being uncastrated, tend to be more dominant and can be aggressive, especially around other horses. They require experienced handlers and often more rigorous training. Geldings, on the other hand, are more docile and predictable, making them suitable for riders of all skill levels.
Mare vs. Filly
Mares and fillies share many characteristics, but their behavior and needs can vary significantly. Mares are mature and can be used for breeding, whereas fillies are still developing. Understanding these differences can help in providing appropriate care and training at different stages of their lives.
Colt vs. Stallion
Colts are young and full of energy, which can sometimes translate to unruly behavior. As they mature into stallions, their behavior can become more pronounced, necessitating more control and training. Proper management during their younger years is crucial to ensure they develop into manageable adults.
Colt (Horse) Genders
The term “colt” specifically refers to young male horses. Understanding colt genders involves recognizing the developmental stages they go through and how their behavior evolves over time.
Training and Socialization
Colts require consistent training and socialization to curb potential aggressive or unruly behaviors. Early training helps in establishing boundaries and ensures they grow into well-behaved adults.
Hormonal Changes
As colts mature, they experience hormonal changes that can affect their behavior. Recognizing these changes and adjusting training methods accordingly is essential for effective management.
Nutritional Needs
Colts have specific nutritional needs that differ from adult horses. Providing a balanced diet that supports growth and development is crucial for their health and well-being.
Types of Horse Genders
Different types of horse genders require tailored approaches to care and management. Understanding these types helps in creating a suitable environment for each horse.
Breeding Considerations
When considering breeding, understanding the types of horse genders is essential. Stallions and mares used for breeding need specific care to ensure successful mating and healthy offspring.
Behavioral Traits
Each horse gender exhibits unique behavioral traits that can impact training and handling. Recognizing these traits helps in developing effective training strategies and creating a harmonious environment for all horses.
Health and Wellness
Health care requirements can vary based on horse gender. Regular veterinary check-ups and appropriate medical care tailored to each gender’s needs are essential for maintaining their overall health.
Comparison of Horse Genders
| Gender | Age Group | Characteristics | Primary Uses |
| Stallion | Mature male, 4+ | Aggressive, dominant, muscular build | Breeding |
| Mare | Mature female, 3+ | Nurturing, strong-willed, can be used for breeding and various tasks | Breeding, riding |
| Gelding | Castrated male | Calm, steady temperament, predictable | Riding, work |
| Colt | Young male, <4 | Energetic, challenging, requires training and socialization | Developing for riding |
| Filly | Young female, <4 | Playful, curious, needs training | Developing for riding |
| Foal | Either gender, <1 | Dependent, requires nurturing and careful handling | Development |
Wrapping Up
Understanding horse genders is vital for anyone involved in horse care, riding, or breeding. By recognizing the differences in behavior, needs, and characteristics across various horse genders and ages, you can ensure your horses receive the best possible care and training.
Whether you’re managing a spirited colt or a nurturing mare, this guide provides the insights needed to foster a positive and productive relationship with your horses.
In conclusion, knowing the nuances of horse genders can make a significant difference in how you care for and interact with these magnificent animals.
With the right knowledge and approach, you can enhance your horse-riding experience and ensure the well-being of your equine companions.
